PROJECT: Heart²
The purpose of this document is to document the contribution that I have made in the project: Heart² as a student undertaking the module CS2103T under NUS School of Computing.
Heart² github link: https://github.com/CS2103-AY1819S1-F10-3/main
1. Introduction
Heart² is a desktop software aiming to make the job of wedding planning agencies simpler. It provides simple yet powerful features to efficiently manage clients' and agency companies' profiles. Users can find suitable wedding service providers for clients using just a few keystrokes with our enterprise feature set.
The project is written in Java and has about 10 thousand lines of code. The user interacts with the application mainly using a Command Line Interface (CLI), and it also has a Graphic User Interface (GUI) created with JavaFX for users who are not so adept with the keyboard.
2. Summary of contributions
Below is a summary of the contributions that I have made to the project. |
2.1. Major Enhancement
-
Major enhancement: Revamp the
listcommand. -
Functionality: The user is able to use the
listcommand to list all clients or vendors. They are also able to use the command to search through clients and vendors by providing the relevant keywords that they want to search for. -
Justification: By having both the searching and listing functionality in one command the user will have less commands to familiarise with and it increases the ease of use of the application.
-
Highlights: To revamp the
listcommand, I need to have a deep understanding of how the commands work as well as how the parser works, which I spent time to familiarise myself with. I also had to change how some of the information was stored in the application, so that the relevant information could be retrieved easily when needed. -
Functional Code Contributed: all code
-
Test Code Contributed: all tests
2.2. Minor Enhancement
-
Minor enhancement: Enhance
undoandredocommands to display the list which was modified. -
Functionality: The list shown to the user after executing the
undoandredocommands will be the list of clients or vendors that was changed through the command. -
Justification: This is to allow the user to be able to see what was changed at a glance without needing to navigate to the corresponding list.
-
Functional Code Contributed: all code
-
Test Code Contributed: all tests
2.3. Other Contributions
-
Community:
-
Reported bugs and provide suggestions to other team members' code. Check it out here.
-
-
Tools:
-
Set up Netlify.
-
-
Documentation:
-
Wrote the about us documentation.
-
Contributed to the User Guide and Developer Guide for this project. See below for more details.
-
-
Summary of contributions:
-
Over 35 Pull Requests on Github.
-
Over 25 Issues raised on Github.
-
Over 30 Reviews of Pull Requests on Github.
-
Overview of all contributions.
-
3. Contributions to the User Guide
Below are sections I contributed to the User Guide. They showcase my ability to write documentation targeting end-users. |
3.1. Listing and searching for contacts: list
You can view all the contacts of a specific type in a list by specifying the contact type to be shown.
Format: <CONTACT_TYPE> list
|
|
|
|
Heart² also supports searching via name, phone number, email, address and tags for you to quickly find your contacts. To search, simply append your search parameters to the back of the original command.
Only contacts that matches all the search parameters will be displayed to you in the form of a list. Searching is done through substring matching, so you do not need to enter the full name, just part of the name will do.
Format: <CONTACT_TYPE> list [n/FULL_NAME] [p/PHONE_NUMBER] [e/EMAIL_ADDRESS] [a/HOME_ADDRESS] [t/TAG]…
|
|
|
|
3.2. Undo the previous command: undo
Undo the commands that you have entered in chronological order for this particular session. Once you logout or exit the application, you cannot undo a command from the last session.
Format: undo
The application will only undo commands that modifies the list of contacts: add, update, delete, clear
|
| The application will show either the client list or vendor list corresponding to the command that was undone. |
3.3. Redo the commands undone: redo
Redo the commands that you have undone by undo in chronological order for this particular session. Once you logout or exit the application, you cannot redo a command from the last session.
Format: redo
Commands that have been undone will be reset upon a clear command.
|
| The application will show either the client list or vendor list corresponding to the command that was redone. |
3.4. Command summary
Below is a summary of the commands available for you to use.
Before logging in
| FEATURE | FORMAT |
|---|---|
To get help |
|
To log in |
|
To close the application |
|
After logging in
| FEATURE | FORMAT |
|---|---|
To register a new account |
|
To change your account password |
|
To add a contact |
|
To add a service requirement |
|
To update a specific contact |
|
To list contacts that matches the inputs |
|
To find a match that fits a particular contact’s requirements |
|
To view a specific contact |
|
To delete a specific contact |
|
To delete all contacts |
|
To list all the commands entered in this session |
|
To undo the previous command |
|
To redo the previous undone command |
|
To get help |
|
To log out of your account |
|
To close the application |
|
4. Contributions to the Developer Guide
Below are sections I contributed to the Developer Guide. They showcase my ability to write technical documentation and the technical depth of my contributions to the project. |
4.1. List Feature
Heart² allows you view all the clients or the vendors with a simple command: list.
When listing contacts, you would have to specify whether the contact is a client or a vendor by prefixing it to list:
-
client list -
vendor list
Below shows an example of how listing all clients works:
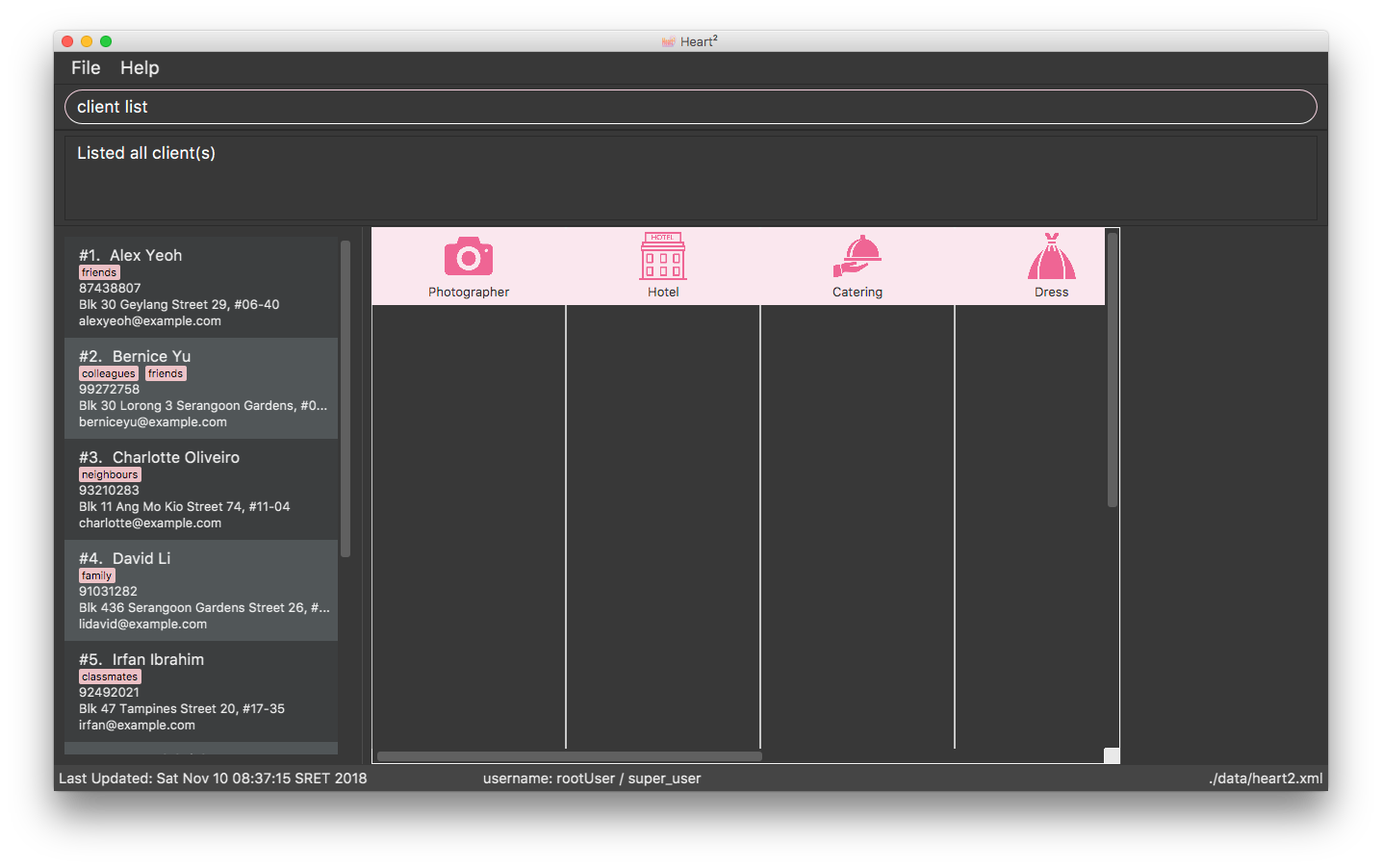
Furthermore, you are also able to add keywords after the list to do filtering, and each keyword is specified to belong to a category and only contacts which contains all of the keywords in their respective categories will be shown.
|
Categories include:
|
Below shows an example of how list filtering works:
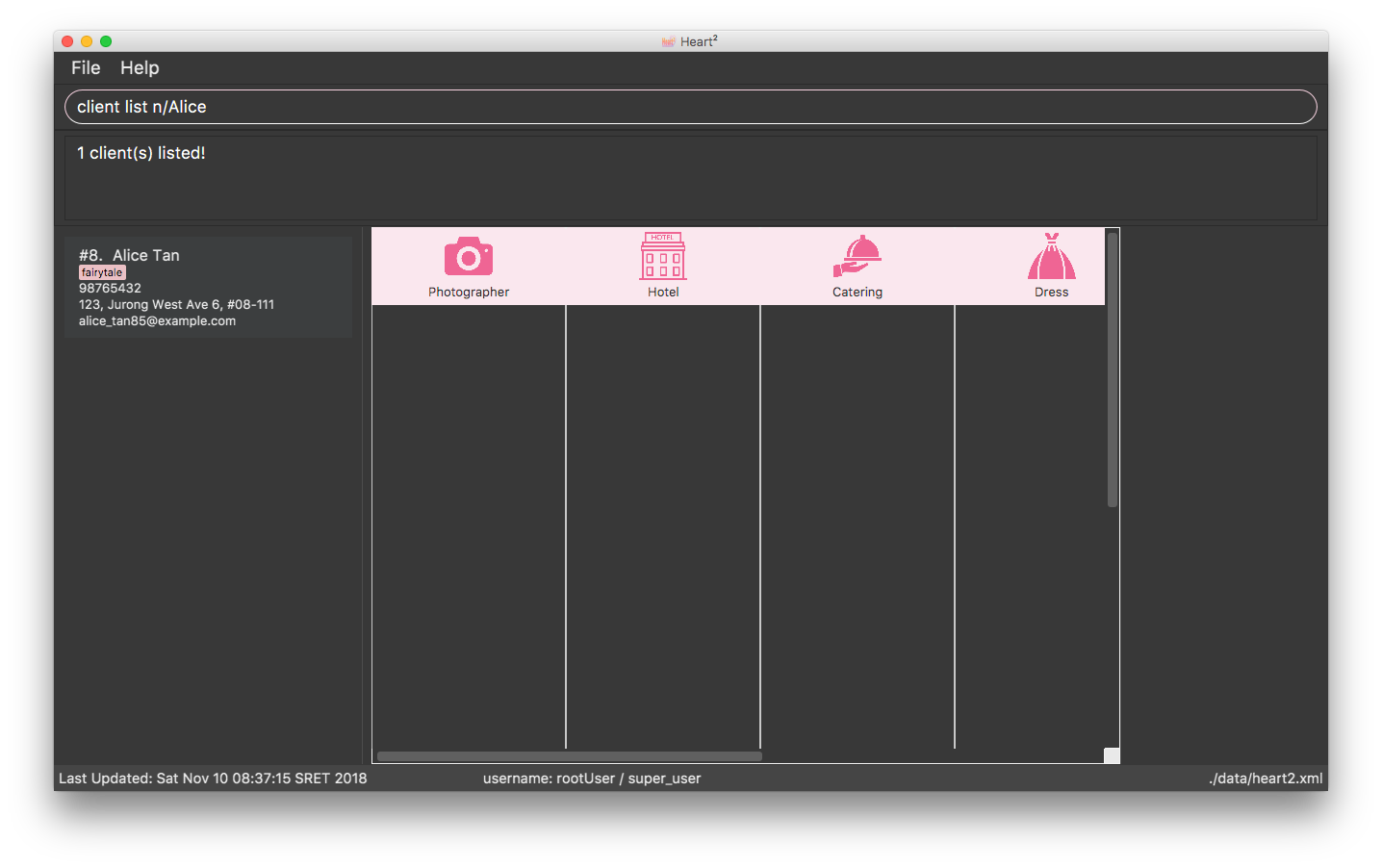
4.1.1. Implementation
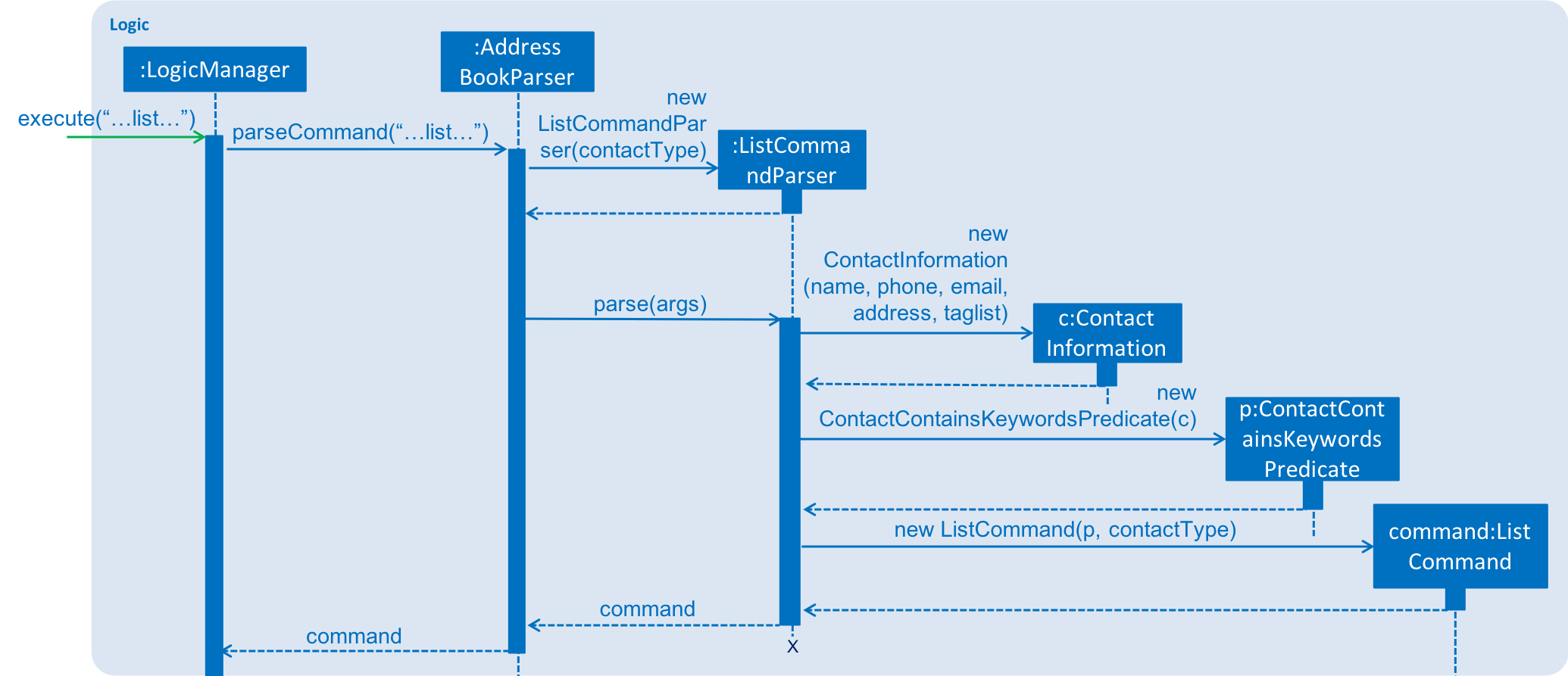
The keywords from the command to be used for filtering is parsed by the ListCommandParser into a ContactInformation
and passed to a Predicate to be used for filtering. The Predicate is implemented as ContactContainsKeywordsPredicate.
Below is a sequence diagram showing the creation of the ListCommand.
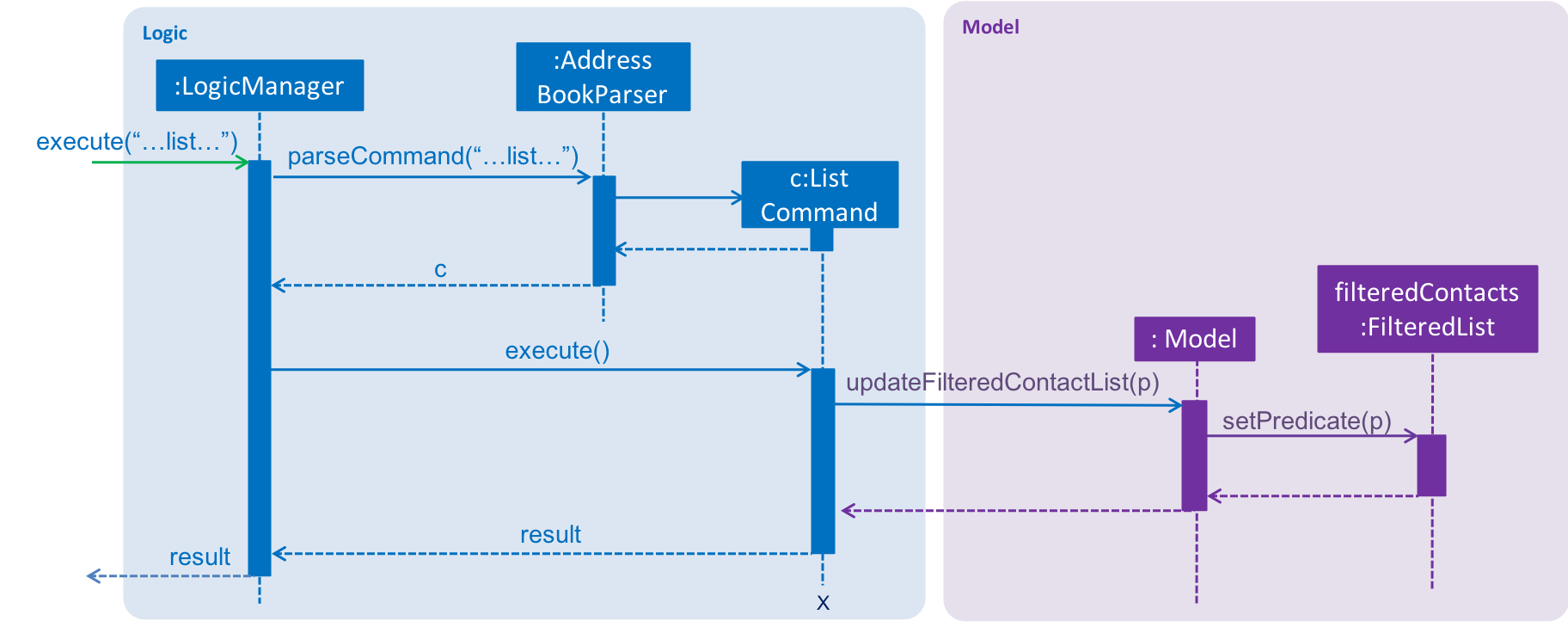
We use a FilteredList and pass the combination of 2 Predicates into it, one to filter the type of contact,
clients or vendors and the other is to filter by keywords, which is the ContactContainsKeywordsPredicate from the ListCommandParser.
Below is a sequence diagram showing the execution of the ListCommand.
Aspect 1: Substring Matching or Word Matching
-
Alternative 1 (current choice): Substring matching.
-
Pros: Users would be able to view a wider range of results that matches the substring they have given. Easier to use.
-
Cons: Irrelevant results might not be filtered away if they contain the substring.
-
-
Alternative 2: Word matching.
-
Pros: Guarantees that no irrelevant results are shown.
-
Cons: Relevant results that have a small difference in the wording will be filtered away and not shown.
-
Aspect 2: Categorised or Non-categorised keywords
-
Alternative 1 (current choice): Categorised keywords.
-
Pros: Users are able to specify which keywords they want to search for in which category. Gives better control over the searching.
-
Cons: Users have to follow a specific format to type the keywords.
-
-
Alternative 2: Non-categorised keywords.
-
Pros: User can type in the keywords in any order they want. Easier to use.
-
Cons: Irrelevant results that contains the keywords will be shown.
-
Aspect 3: All Match or Any Match
-
Alternative 1 (current choice): All match.
-
Pros: Users can specify what they want to search for and filter out all irrelevant results.
-
Cons: Users are not able to search for multiple things, when they only require one of them to match.
-
-
Alternative 2: Any match.
-
Pros: Users are able to obtain a wider search result. Easier to use.
-
Cons: Irrelevant results that contains only one or a few keywords will be shown as well.
-
4.2. Undo and Redo Aspect: What it shows after undo/redo command successfully executes
-
Alternative 1 (current choice): Shows the list that was changed due to the undo/redo command.
-
Pros: Easy for the user to identify what was changed, whether a client or vendor was modified.
-
Cons: It switches the list out of the current filter and the user have to re-type the list command if he wants to filter the list.
-
-
Alternative 2: Keeps showing what was shown before the command was executed.
-
Pros: Easy to implement.
-
Cons: Hard for the user to identify what was changed in the addressbook.
-
-
Alternative 3: Show what was changed, before and after.
-
Pros: User can easily tell what was changed.
-
Cons: Hard to implement, need to have an additional UI components to show what was changed and need additional components to store the list before it was changed.
-
4.3. Use Cases
4.3.1. Use case: List all the Clients or Vendors
Preconditions: User is logged in with a SUPER_USER account.
MSS
-
User enters the list command and requests to view either all the Clients, or all the Vendors.
-
System returns either a list with all the Clients' information, or all the Vendors' information.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
2a. There is no Client or no Vendor available
-
2a1. System returns an empty list.
Use case ends.
-
4.3.2. Use case: Filter and show Client’s or Vendor’s info according to the filter
Preconditions: User is logged in with a SUPER_USER account.
MSS
-
User enters the list command and requests to view either Client’s or Vendor’s information with some keywords provided indicated by prefixes.
-
The System displays a list of Clients or Vendors whose information matches what was provided.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
1a. User enters a prefix that does not exist.
-
1a1. System prompts the User the correct format of the command and prefixes that can be used.
-
-
1b. User enters an empty prefix.
-
1b1. System prompts the User the correct format of the command and prefixes that can be used.
Use case ends.
-
